Django Vue.js and GraphQL - Step by step
Instruction
This is not a tutorial with every detailed information about each framework. I’ve described only points about configuration and why it is done. You should have installed
node.jsshorbashfor running.shscripts (you can do it manually bypython manage.py runserver)pythonversion >= 3
The whole project can be found in the github page:
https://github.com/alexiej/django-vue-graphql
To do:
- Add working Unit Tests
- Add working e2e Tests
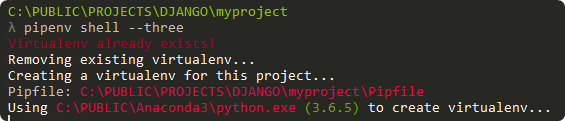
1. Create Django project
mkdir myproject
cd myproject
pipenv shell --three
pipenv install django
django-admin startproject myproject .
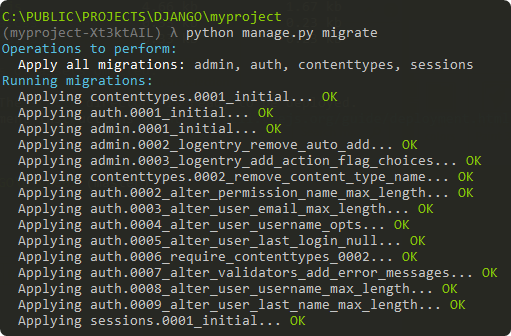
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py createsuperuser
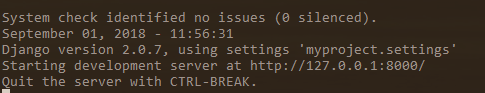
python manage.py runserver
`http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/`
2. Split Configuration into production and development
__init__.pydev.py, andprod.py
BASE_DIR - because we move our file to the subfolder we need to change BASE_DIR
STATIC_ROOT - is the folder where files after collectstatic go.
myproject\settings.py
BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(
os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "staticfiles")
from .dev import *
from .settings import *
DEBUG = True
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['127.0.0.1', 'localhost']
from .settings import *
DEBUG = False
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']
run.sh
These 3 commands are commands to synchronise all our changes with the server before running.
collectsatic- move all static files to theSTATIC_ROOTfoldermakemigrations- create new migration based on changes you have made to your modelsmigrate- apply migration
#!/bin/bash
pipenv shell
case $1 in
dev)
python manage.py runserver --settings=myproject.settings.dev
;;
prod)
python manage.py collectstatic --noinput
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py runserver --settings=myproject.settings.prod
;;
esac
sh run.sh dev
sh run.sh prod
You’ve got “Not Found ”because you haven’t specified default url yet.
3. Create home page
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
Home page
</body>
</html>
mypproject\settings\settings.py
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates'),
],
...
myproject\url.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.views.generic import TemplateView
urlpatterns = [
path('', TemplateView.as_view(template_name='index.html')),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
]
sh run.sh dev
sh run.sh prod
4. Add Django Debug Toolbar
pipenv install django-debug-toolbar
myproject\settings\dev.py
MIDDLEWARE.append('debug_toolbar.middleware.DebugToolbarMiddleware')
INSTALLED_APPS.append('debug_toolbar')
INTERNAL_IPS = ('127.0.0.1', 'localhost')
myproject\urls.py
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls import include, url
...
if settings.DEBUG:
import debug_toolbar
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^__debug__/', include(debug_toolbar.urls)),
] + urlpatterns
5. Add vue.js frontend
npm i -g @vue/cli
vue create frontend
Install additionally:
vue-router(Use history mode for router?:yes)
cd frontend
yarn serve
6. Integrate with the Django project
npm install webpack-bundle-tracker --save-dev
npm install write-file-webpack-plugin --save-dev
pipenv install django-webpack-loader
var BundleTracker = require('webpack-bundle-tracker')
var WriteFilePlugin = require('write-file-webpack-plugin')
module.exports = {
outputDir: (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production" ? 'dist' : 'static'),
baseUrl: '/',
devServer: {
publicPath: "http://localhost:8080/",
headers: {
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin": "*",
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods": "GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, PATCH, OPTIONS",
"Access-Control-Allow-Headers": "Origin, X-Requested-With, Content-Type, Accept, Accept-Encoding, Accept-Language, Access-Control-Request-Headers, Access-Control-Request-Method",
"Access-Control-Allow-Credentials": "true"
}
},
chainWebpack: config => {
config.optimization.splitChunks({
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
name: 'chunk-vendors',
test: /[\\\/]node_modules[\\\\/]/,
priority: -10,
chunks: 'initial'
},
common: {
name: 'chunk-common',
minChunks: 2,
priority: -20,
chunks: 'initial',
reuseExistingChunk: true
}
}
})
},
configureWebpack: {
output: {
filename: 'js/[name].js',
chunkFilename: 'js/[name].js'
},
plugins: [
new WriteFilePlugin(),
(process.env.NODE_ENV === "production" ?
new BundleTracker({
filename: 'webpack-stats-prod.json',
publicPath: '/'
}) :
new BundleTracker({
filename: 'webpack-stats.json',
publicPath: 'http://localhost:8080/'
})
)
]
}
}
baseUrl: “./”: This is how the webpack will generate all links inside. ./ means that there is no begining slash and all links come from the current folder. This configuration won’t work for router apps where browser will download link from the subpage. (for example img/logo2.png in url http://127.0.0.1:8000/about/ will download a file from the http://127.0.0.1:8000/about/img/logo2.png which is not correct)
if baseUrl: "/" then all links will be downloaded from the host url. If you have your webpage in a folder (not main host) you need to change this configuration to the basefolder where you host your vue.js files. (like /username/mypage)
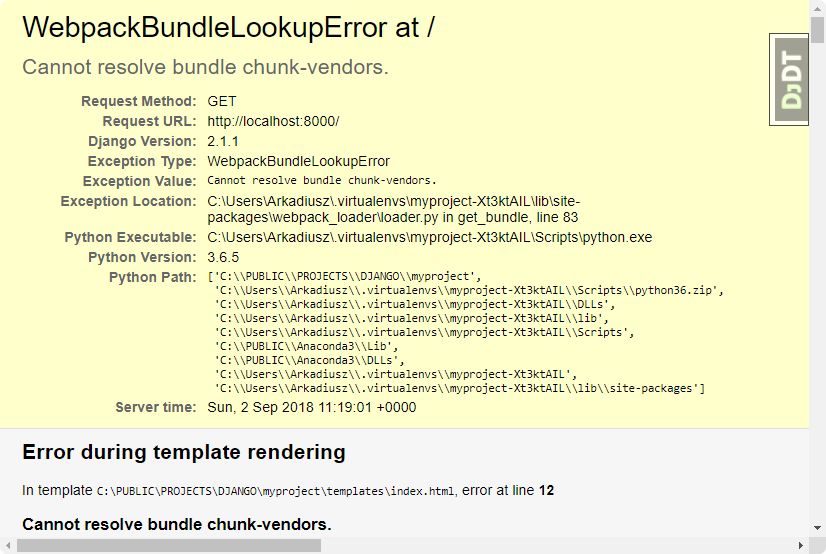
BundleTracker will generate webpack-stats.json for you project that will be used in the Django project. (for production and development)
outputDir - this is where all files will be used by the Djange project (static or dist)
output, chainWebpack - because we don’t use default .html from .vue we need to have the same list of chunks to load in the production and development environemt (from webpack-stats.json and webpack-stats-prod.json)
WriteFilePlugin - this plugin will copy files to the destination folder even when we run webpack-dev-server. This is important because Django use static files like images from this folder.
vue inspect > output-dev.js
vue inspect --mode production > output-prod.js
output-dev.js
output: {
path: 'C:\\PUBLIC\\PROJECTS\\DJANGO\\myproject\\frontend\\static',
filename: 'js/[name].js',
publicPath: '/',
chunkFilename: 'js/[name].js'
},
...
optimization: {
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
name: 'chunk-vendors',
test: /[\\\/]node_modules[\\\\\/]/,
priority: -10,
chunks: 'initial'
},
common: {
name: 'chunk-common',
minChunks: 2,
priority: -20,
chunks: 'initial',
reuseExistingChunk: true
}
}
}
},
output-prod.js
output: {
path: 'C:\\PUBLIC\\PROJECTS\\DJANGO\\myproject\\frontend\\dist',
filename: 'js/[name].js',
publicPath: '/',
chunkFilename: 'js/[name].js'
},
...
splitChunks: {
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
name: 'chunk-vendors',
test: /[\\\/]node_modules[\\\\\/]/,
priority: -10,
chunks: 'initial'
},
common: {
name: 'chunk-common',
minChunks: 2,
priority: -20,
chunks: 'initial',
reuseExistingChunk: true
}
}
}
myproject\settings\settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'webpack_loader'
]
myproject\settings\dev.py
from .settings import *
DEBUG = True
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']
MIDDLEWARE.append('debug_toolbar.middleware.DebugToolbarMiddleware')
INSTALLED_APPS.append('debug_toolbar')
INTERNAL_IPS = ('127.0.0.1', 'localhost')
WEBPACK_LOADER = {
'DEFAULT': {
'BUNDLE_DIR_NAME': '',
'STATS_FILE': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'frontend/webpack-stats.json'),
}
}
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static"),
]
MEDIA_URL = '/dmedia/'
MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "mediafiles")
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "staticfiles")
VUE_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "frontend\\static\\")
myproject\settings\prod.py
from .settings import *
import os
DEBUG = False
ALLOWED_HOSTS = ['*']
WEBPACK_LOADER = {
'DEFAULT': {
'BUNDLE_DIR_NAME': '',
'STATS_FILE': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'frontend/webpack-stats-prod.json'),
}
}
STATICFILES_DIRS = [
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static"),
]
MEDIA_URL = '/dmedia/'
MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "mediafiles")
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "staticfiles")
VUE_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "frontend\\dist\\")
BUNDLE_DIR_NAMEset up your prefix for every chunk. This a prefix for.jsand.cssfiles. The setting should be empty for our configuration and match with thebaseUrlfrom thevue.config.js.STATS_FILE- file to load webpack statistics.MEDIA_URL- Media files from Django (dmediabecuasevue.jshas alsomediafolder formp4|webm|ogg|...files)MEDIA_ROOT- Path where media files will be uploaded by a userSTATIC_URL- Url for static files in Django.SATIC_ROOT- Where all files will be copied inpython manage.py collectstaticprocedureVUE_ROOT- helpful path for allvue.jsoutput. This must match with thevue.jsproject destination folder.
mkdir static
myproject\urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.views.generic import TemplateView
from django.conf import settings
from django.conf.urls import include, url
from django.views.static import serve
import os
urlpatterns = [
path('', TemplateView.as_view(template_name='index.html')),
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
url(r'^static/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,
{'document_root': settings.STATIC_ROOT}),
url(r'^dmedia/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,
{'document_root': settings.MEDIA_ROOT}),
url(r'^media/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,
{'document_root': os.path.join(settings.VUE_ROOT, 'media')}),
url(r'^img/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,
{'document_root': os.path.join(settings.VUE_ROOT, 'img')}),
url(r'^js/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,
{'document_root': os.path.join(settings.VUE_ROOT, 'js')}),
url(r'^css/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,
{'document_root': os.path.join(settings.VUE_ROOT, 'css')}),
url(r'^fonts/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,
{'document_root': os.path.join(settings.VUE_ROOT, 'fonts')}),
]
if settings.DEBUG:
import debug_toolbar
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^__debug__/', include(debug_toolbar.urls)),
] + urlpatterns
all urls are similar to what can be found in the destination vue.js project. We use dmedia for django media because vue.js use the same folder for media files.
/myproject/urls.py
import os
from django.views.generic.base import RedirectView
favicon_view = RedirectView.as_view(url=os.path.join(settings.STATIC_URL,'favicon.ico'), permanent=True)
urlpatterns = [
path('favicon.ico', favicon_view),
...
{% load render_bundle from webpack_loader %}
{% load static from staticfiles %}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>frontend</title>
<meta http-equiv=X-UA-Compatible content="IE=edge">
<meta name=viewport content="width=device-width,initial-scale=1">
<link rel=icon href="{% static 'favicon.ico' %}"> {% render_bundle 'chunk-vendors' %}
</head>
<body><noscript><strong>We're
sorry but frontend doesn't work properly without JavaScript enabled. Please enable it to
continue.</strong></noscript>
{% for i in 'abc' %}
<strong>{{ i }} DJANGO PART</strong>
{% endfor %}
<div id=app>
</div>
{% render_bundle 'app' %}
</body>
</html>
{% render_bundle 'chunk-vendors' %} - this is a loader for splitChunks in the development and production environment. If we don’t configure splitChunks for dev Django will show you an error message.
The main vue.js application
<div id=app>
</div>
{% render_bundle 'app' %}
...
npm run serve in the frontend folder
sh run.sh dev in the django folder
npm run build in the frontend folder
sh run.sh prod in the django folder
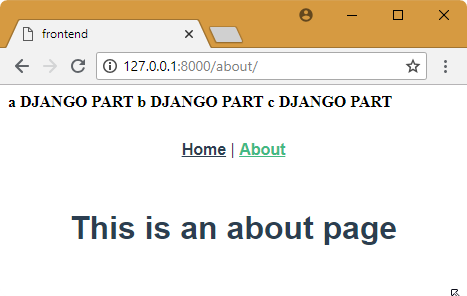
npm run serve in the frontend folder
sh run.sh dev in the django folder
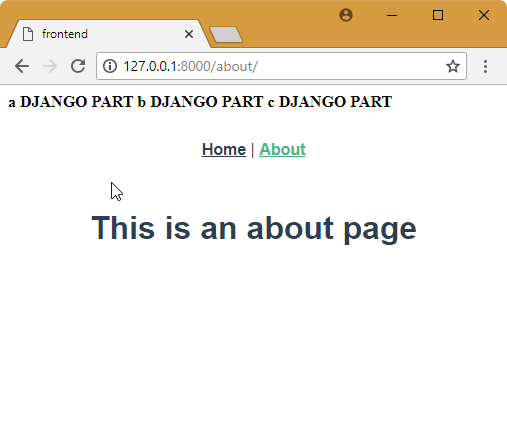
7. Add url for About page
About page works only in the Single Page Application main page. When we want working url for http://127.0.0.1:8000/about, we need to add url for about page.
...
urlpatterns = [
path('', TemplateView.as_view(template_name='index.html')),
path('about/', TemplateView.as_view(template_name='index.html')),
....
http://127.0.0.1:8000/about/
8. Integrate Django with GraphQL
pipenv install graphene_djangopipenv install django-filter==1.1.0
django-admin startapp tasks
myproject/tasks/models.py
from django.db import models
from django.contrib import admin
# Create your models here.
class Task(models.Model):
isDone = models.BooleanField()
name = models.CharField(max_length=100)
description = models.TextField()
def __str__(self):
return self.name
@admin.register(Task)
class TaskAdmin(admin.ModelAdmin):
pass
myproject/settings/settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
# Install the ingredients app
'tasks',
]
python manage.py makemigrations
python manage.py migrate
[{
"model": "tasks.Task",
"pk": 1,
"fields": {
"isDone": "True",
"name": "Do shoppping",
"description": "milk, butter"
}
}, {
"model": "tasks.Task",
"pk": 2,
"fields": {
"isDone": "False",
"name": "Do laundry",
"description": "all clothes"
}
}, {
"model": "tasks.Task",
"pk": 3,
"fields": {
"isDone": "False",
"name": "Fix computer",
"description": "Fix computer"
}
}]
python manage.py loaddata tasks
tasks\schema.py
# myproject/tasks/schema.py
import graphene
from graphene_django.types import DjangoObjectType
from graphql_relay.node.node import from_global_id
from tasks.models import Task
class TaskType(DjangoObjectType):
class Meta:
model = Task
class CreateTask(graphene.Mutation):
ok = graphene.Boolean()
task = graphene.Field(lambda: TaskType)
class Arguments:
name = graphene.String()
description = graphene.String()
def mutate(self, info, name, description):
task = Task(name = name, description = description, isDone = False)
task.save()
ok = True
return CreateTask(task=task,ok=ok)
class UpdateTask(graphene.Mutation):
task = graphene.Field(lambda: TaskType)
ok = graphene.Boolean()
class Arguments:
id = graphene.String()
IsDone = graphene.Boolean()
def mutate(self, info, id, IsDone):
task = Task.objects.get(pk=id)
task.isDone = IsDone
task.save()
ok = True
return UpdateTask(task=task,ok=ok)
class Query(graphene.ObjectType):
tasks = graphene.List(TaskType)
def resolve_tasks(self, info):
return Task.objects.all()
class Mutations(graphene.ObjectType):
create_task = CreateTask.Field()
update_task = UpdateTask.Field()
myproject\schema.py
import graphene
import tasks.schema
class Query(tasks.schema.Query, graphene.ObjectType):
# This class will inherit from multiple Queries
# as we begin to add more apps to our project
pass
class Mutation(tasks.schema.Mutations, graphene.ObjectType):
pass
schema = graphene.Schema(query=Query, mutation=Mutation)
myproject\settings\settings.py
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'graphene_django',
]
myproject\settings\settings.py
GRAPHENE = {
'SCHEMA': 'myproject.schema.schema'
}
myproject\urls.py
from graphene_django.views import GraphQLView
from django.views.decorators.csrf import csrf_exempt
urlpatterns = [
...
url(r'^graphql', csrf_exempt(GraphQLView.as_view(graphiql=True))),
]
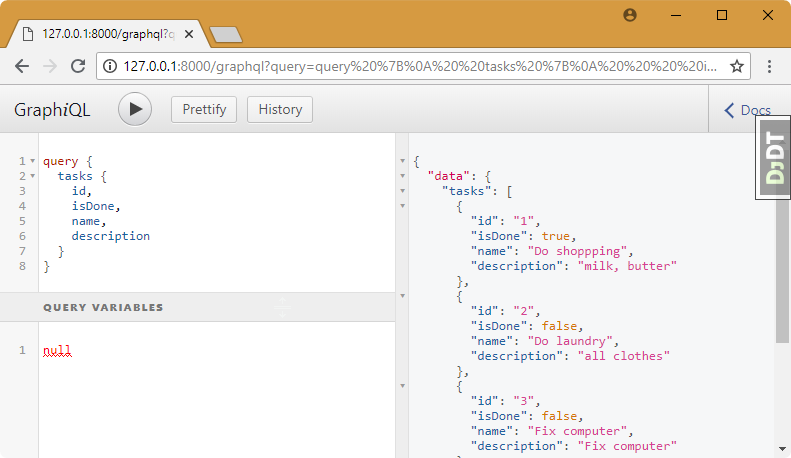
query {
tasks {
id,
isDone,
name,
description
}
}
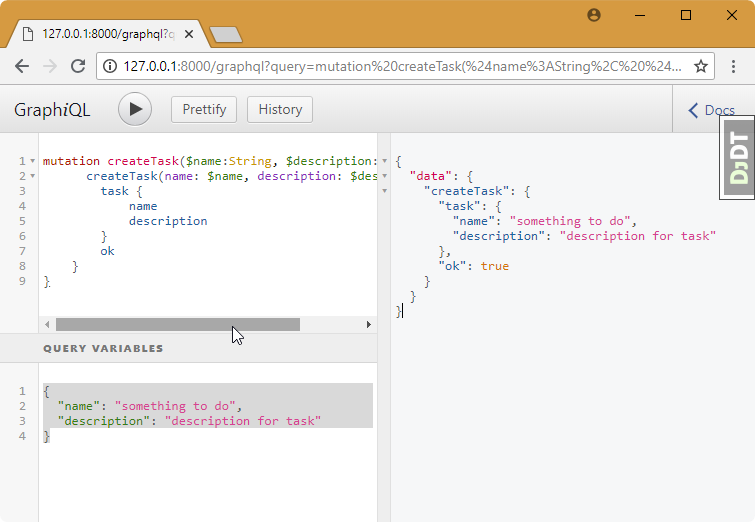
query:
mutation createTask($name:String, $description: String) {
createTask(name: $name, description: $description) {
task {
name
description
}
ok
}
}
variables:
{
"name": "something to do",
"description": "description for task"
}
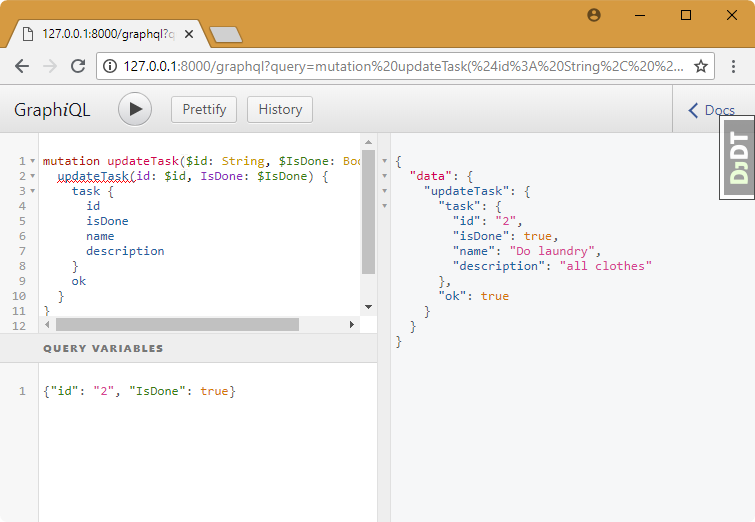
query:
mutation updateTask($id: String, $IsDone: Boolean) {
updateTask(id: $id, IsDone: $IsDone) {
task {
id
isDone
name
description
}
ok
}
}
variables:
{"id": "2", "IsDone": true}
http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/
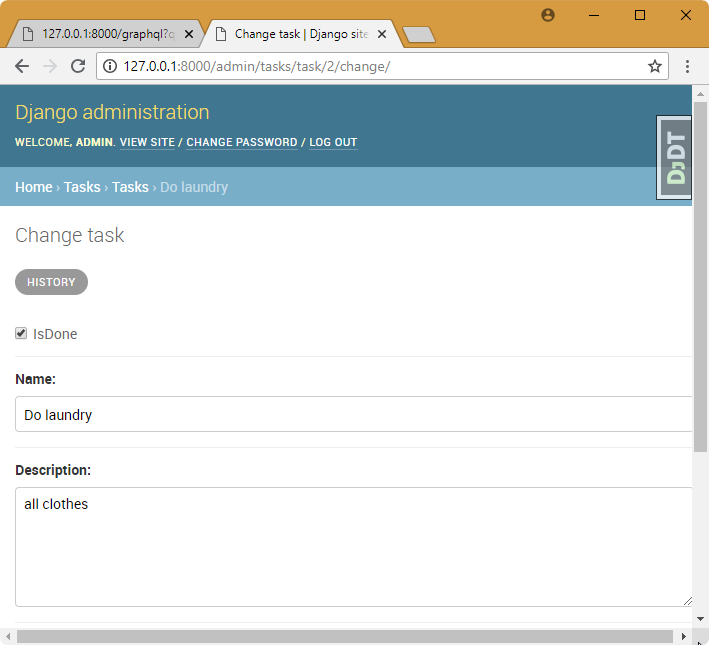
9. Integrate vue.js with graphql
npm install --save vue-apollo graphql apollo-client apollo-link apollo-link-http apollo-cache-inmemory graphql-tag
frontend/src/vue-apollo.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import { ApolloClient } from 'apollo-client'
import { HttpLink } from 'apollo-link-http'
import { InMemoryCache } from 'apollo-cache-inmemory'
import VueApollo from 'vue-apollo'
const httpLink = new HttpLink({
// You should use an absolute URL here
uri: '/graphql',
})
// Create the apollo client
const apolloClient = new ApolloClient({
link: httpLink,
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
connectToDevTools: true,
})
const apolloProvider = new VueApollo({
defaultClient: apolloClient,
})
// Install the vue plugin
Vue.use(VueApollo)
export default apolloProvider
uri: /graphql - This is our urlfor graphql communication with Django.
frontend/src/main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
import apolloProvider from './vue-apollo'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
apolloProvider: apolloProvider,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
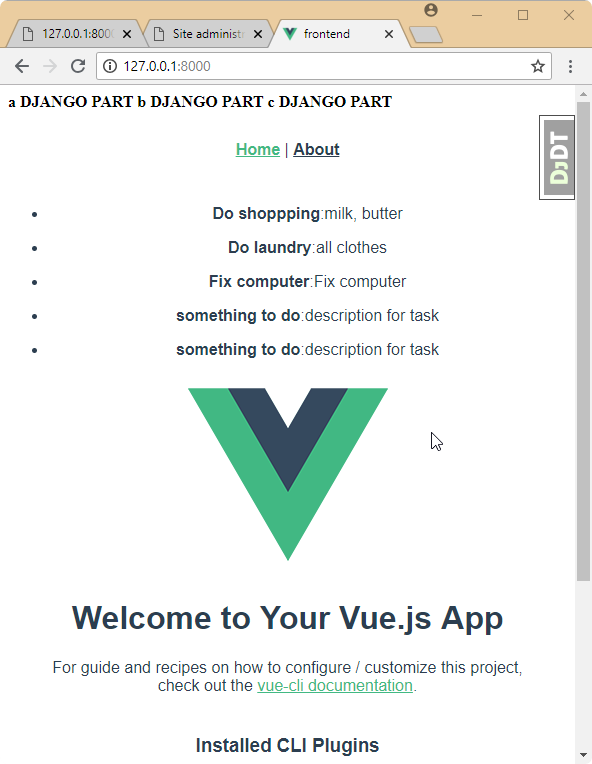
frontend/src/views/Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<div v-for="i in tasks" :key="i.id">
<ul>
<li>
<strong>{{i.name}}</strong>:<span>{{i.description}}</span>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
....
<script>
import gql from 'graphql-tag'
const TaskQuery = gql`
query {
tasks {
id
isDone
name
description
}
}
`;
export default {
data() {
return {
// Initialize your apollo data
tasks: '',
}
},
apollo: {
// Simple query that will update the 'hello' vue property
tasks: TaskQuery,
},
...
npm run serve
sh run.sh dev
npm run build
sh run.sh prod
10. Add create model to vue.js
frontend\src\views\Home.vue
<template>
<div class="home">
<div>
<span>Name:</span><input type="text" v-model="name">
<span>Description:</span><input type="text" v-model="description">
<button @click="create_task">Add</button>
</div>
...
data() {
return {
name: '',
description: '',
...
frontend/.eslintrc.js
module.exports = {
rules: {
'no-console': 'off',
},
};
frontend\src\views\Home.vue
<script>
...
const TaskCreate = gql`mutation createTask($name:String, $description: String) {
createTask(name: $name, description: $description) {
task {
id
isDone
name
description
}
ok
}
}`
frontend\src\views\Home.vue
...
methods: {
async create_task() {
const name = this.name
const description = this.description
// Call to the graphql mutation
let data = await this.$apollo.mutate({
// Query
mutation: TaskCreate,
// Parameters
variables: {
name: name,
description: description
},
update: (store, { data: { createTask } }) => {
// Add to All tasks list
const data = store.readQuery({ query: TaskQuery })
data.tasks.push(createTask.task)
store.writeQuery({ query: TaskQuery, data })
},
// optimisticResponse: {
// __typename: 'Mutation',
// createTask: {
// __typename: 'CreateTask',
// task: {
// __typename: "TaskType",
// id: -1,
// isDone: false,
// name: name,
// description: description
// },
// ok: false
// }
// },
})
var t = data.data.createTask.task
console.log('Added: ' , t)
this.name = ''
this.description = ''
}
...
mutation: query for mutationvariables: variables used in the queryupdate: what happend after an update. Read local cash for queryreadQuerywith queryTaskQuery, insert new data todata.tasksandwriteQueryto refresh local list of tasks.optimisticResponse: Only if it’s necessary to give response before finishing the query to not wait for results.
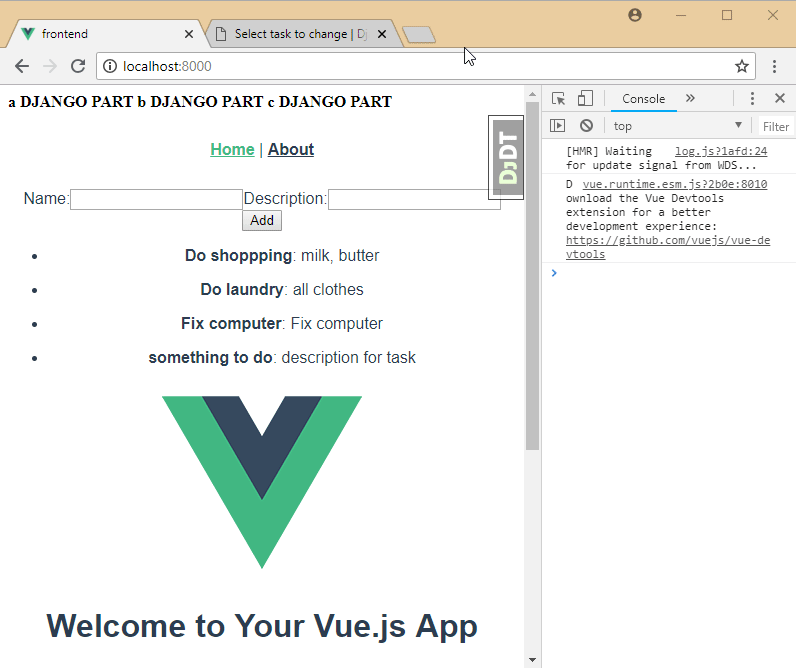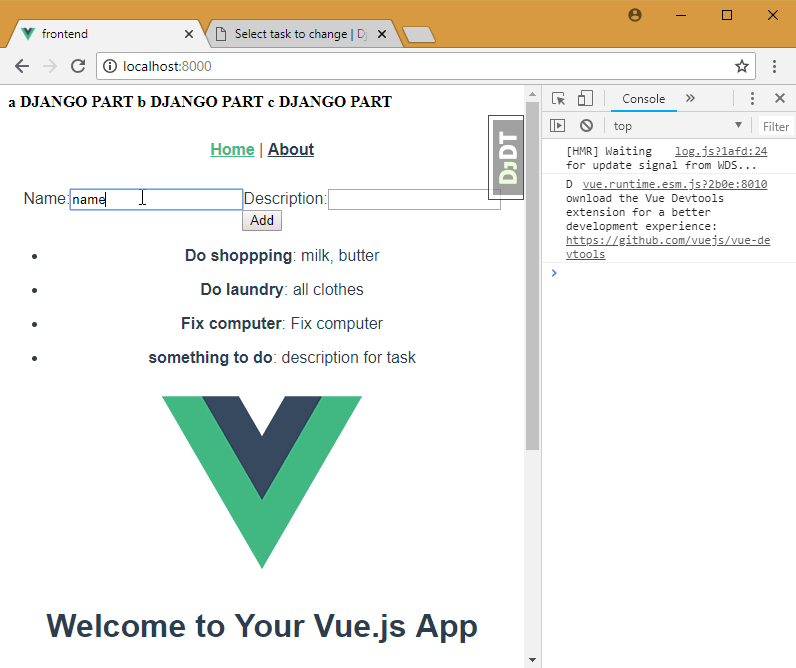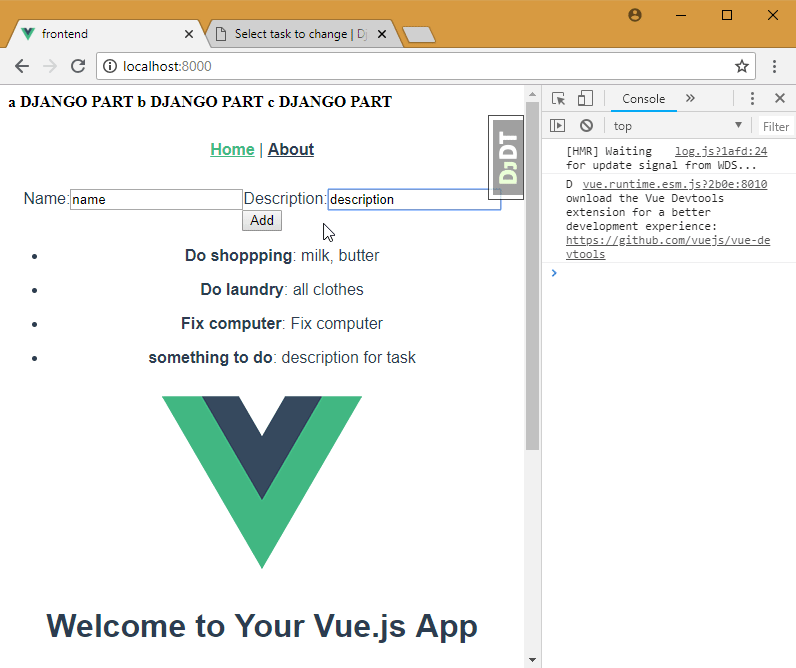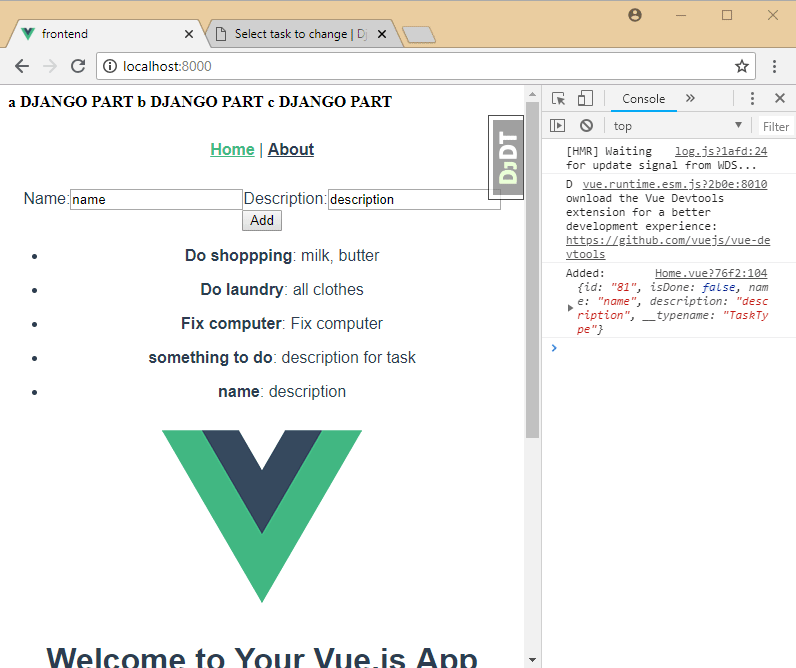
11. Add update model to vue.js
frontend\src\views\Home.vue
...
<div v-for="i in tasks" :key="i.id">
<ul>
<li>
<input type="checkbox" @input="update_task(i)" :checked="i.isDone">
frontend\src\views\Home.vue
<script>
...
const TaskUpdate = gql`mutation updateTask($id: String, $IsDone: Boolean) {
updateTask(id: $id, IsDone: $IsDone) {
task {
id
isDone
name
description
}
ok
}
}`
...
frontend\src\views\Home.vue
methods: {
async update_task(i) {
await this.$apollo.mutate({
mutation: TaskUpdate,
variables: {
id: i.id,
IsDone: !i.isDone
},
})
},
...